Natural diamonds are treasures crafted by nature over billions of years. Deep within the Earth’s mantle, pure carbon atoms bond to form dazzling crystals. Their rarity, brilliance, and unmatched durability make them nature’s most exquisite creation.
Manufacturing Process of Natural Diamonds
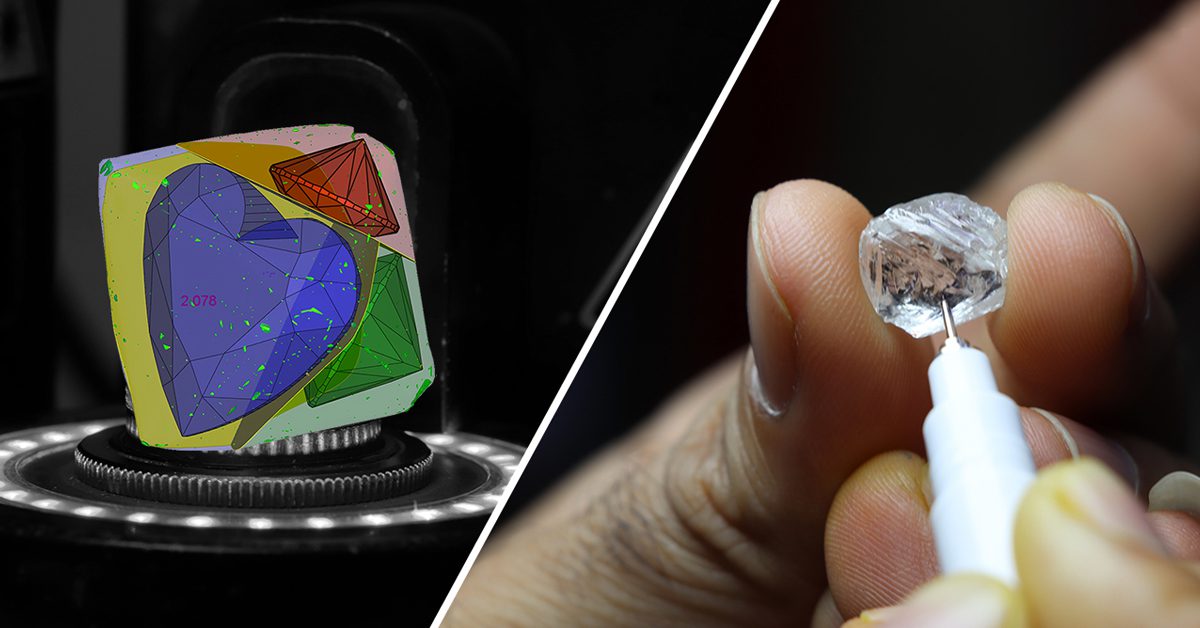
1. Planning the Cut
- Uses Sarin Machine to create 3D models for accurate mapping.
- Expert cutters analyze and mark precise cuts to minimize waste.


2. Marking
- 3D laser technology ensures precision.
- Expert markers strategize cuts around inclusions for optimal clarity.

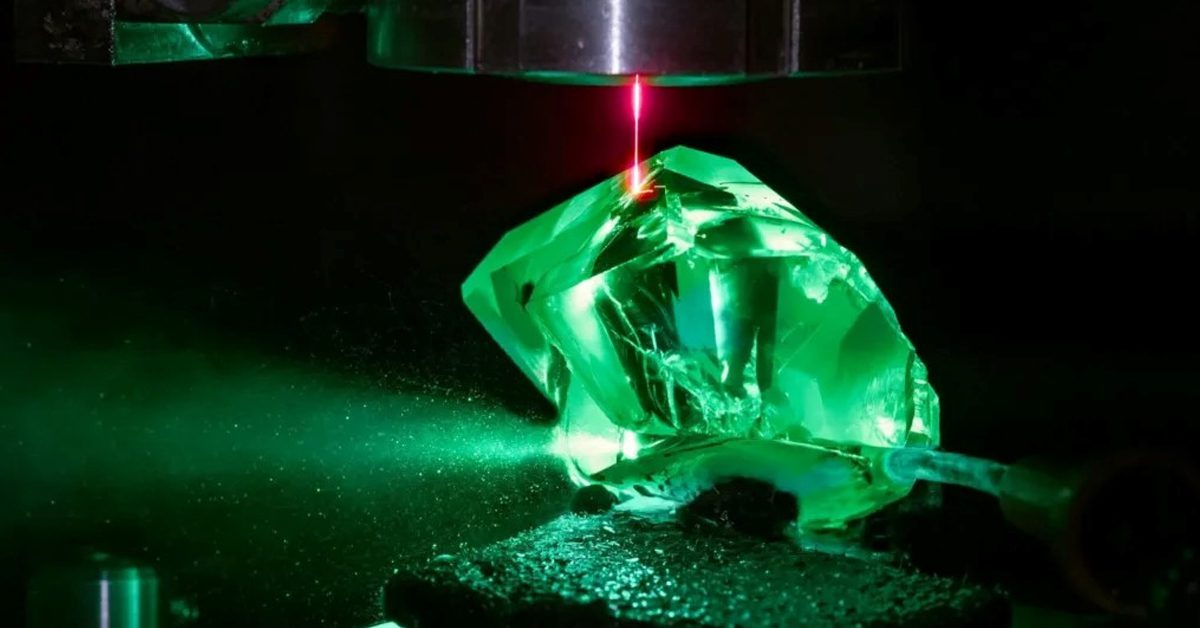
3. Cleaving/Sawing
- Blade Sawing: Coated blades ensure minimal material loss.
- Laser Sawing: High precision with automated cutting.
Manufacturing Process of Natural Diamonds
- Sawing is the separation of a piece of diamond rough into separate pieces, to be finished as individual diamonds after planning the stone.
- In Sawing we use Blade or Laser to cut the rough diamond into separate pieces. This may be used to remove extra portions of the diamond as well.
Blade Sawing
- Blade Sawing is the technology where we cut the diamonds using highly precise diamond powder coated Blades. The advantage is low cutting loss.
Laser Sawing
- Laser Sawing is using highly precise cutting technology with more atomization and making things more precise and accurate.

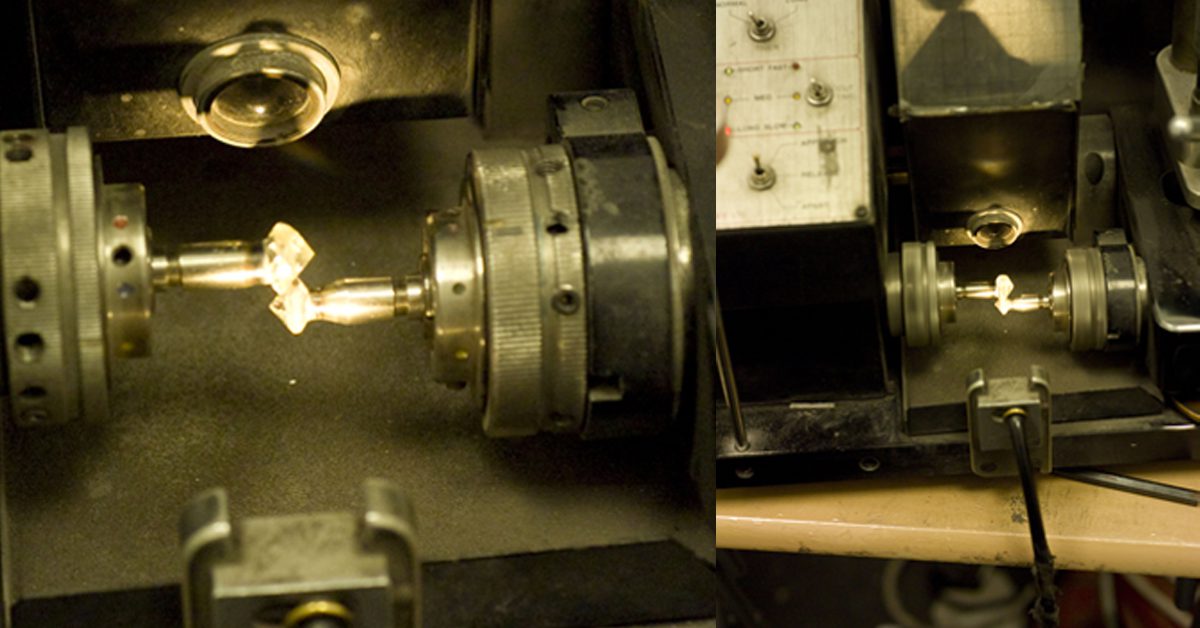
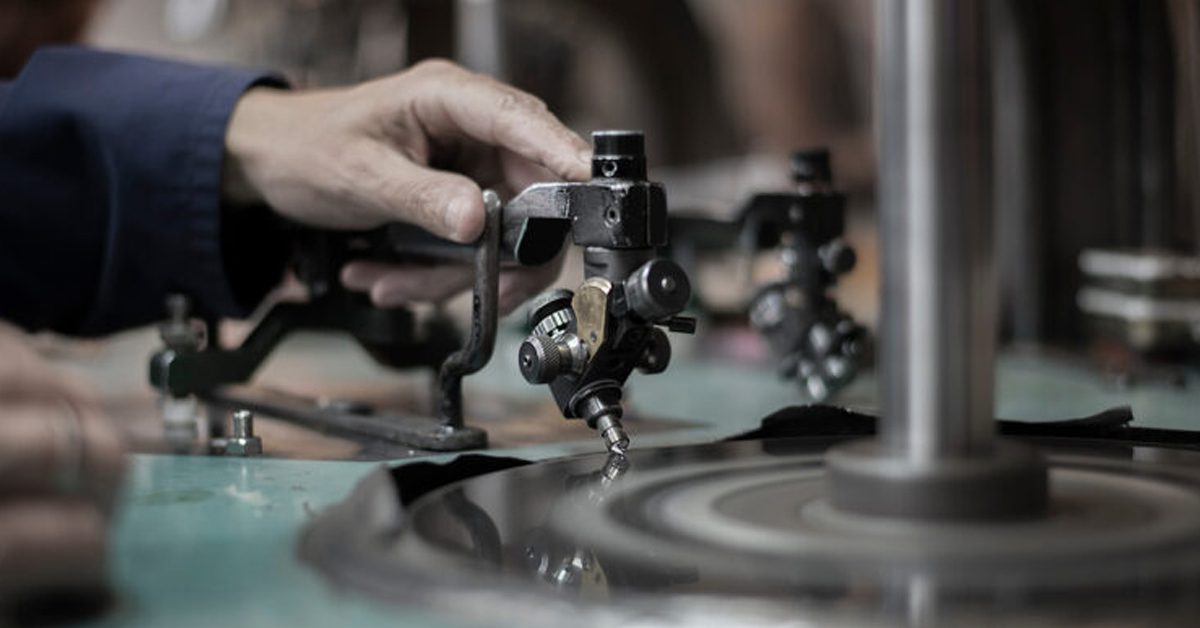
4. Blocking and Bruting
-
Techniques:
- Laser Bruting
- Diamond-on-diamond rubbing
- Disk impregnated with diamond dust.
- Shapes the diamond’s contour with precision.

5. Polishing
- Creates sparkle and scintillation through expertly formed facets.
- Focuses on symmetry and reflection.


6. Certification and Grading Lab
- Diamonds are certified by reputable labs like GIA, IGI, and HRD.
- Strict quality control ensures only the finest gems are offered.

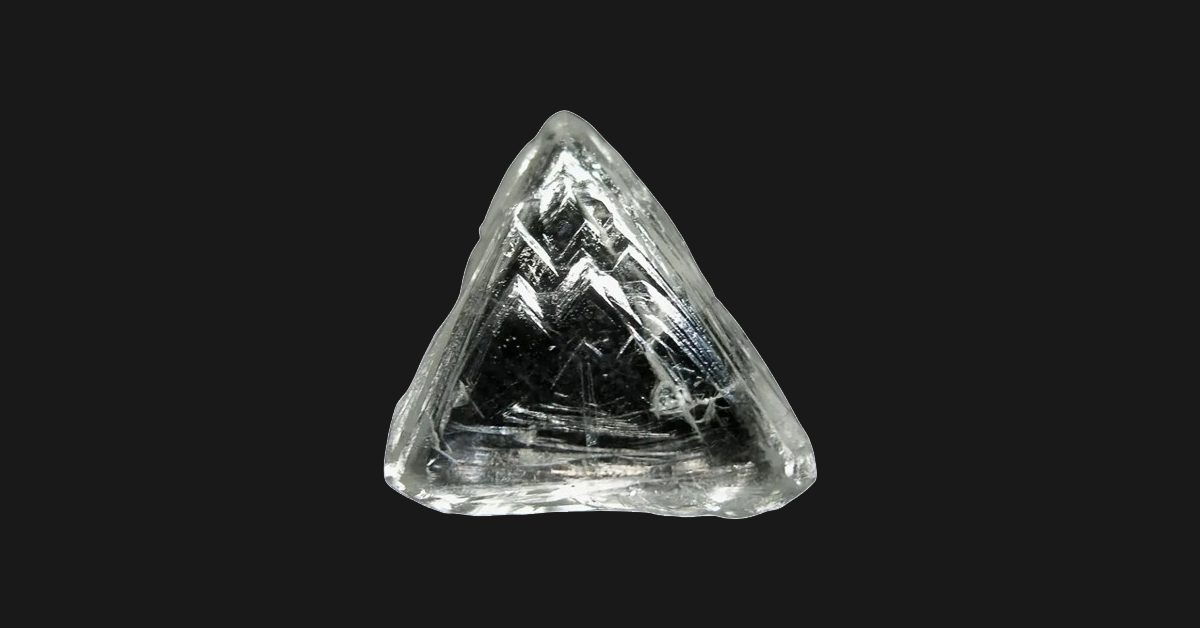
The most complicated stage in the diamond cutting process is planning and analysing the diamond rough, and it also demands the greatest skill and technology. During the design stages, the cutter will choose the best feasible diamond shapes in order to reduce waste and optimize the rough stone’s output. To get precise measurements, the rough stone is often mapped with a Sarin machine. The marker, a highly experienced cutter who weighs all the factors and determines whether a diamond should be sawn or split into pieces, then marks exactly where the cuts should be made, performs these complex computations. This procedure might take months when dealing with huge, expensive gems.
Normally, ‘Sarin Machine’ is used to generate accurate measurements and formulate 3D models that will show the best ways to optimize the rough stone.
The second step in the diamond production process is the marking of the stone using 3D laser technology. Incorrect marking by a fraction of a millimetre can greatly impact the quality of the final diamond, so after noting any imperfections, a diamond marker may decide to work around an inclusion to polish a few high clarity diamonds from one rough stone, rather than yielding one large diamond of lower clarity grading.
Manufacturing Process of Natural Diamonds
- Sawing is the separation of a piece of diamond rough into separate pieces, to be finished as individual diamonds after planning the stone.
- In Sawing we use Blade or Laser to cut the rough diamond into separate pieces. This may be used to remove extra portions of the diamond as well.
Blade Sawing
- Blade Sawing is the technology where we cut the diamonds using highly precise diamond powder coated Blades. The advantage is low cutting loss.
Laser Sawing
- Laser Sawing is using highly precise cutting technology with more atomization and making things more precise and accurate.
Once the rough diamond has been reduced to the desired measurements by sawing, it needed to be contoured to achieve the basic shape through the process called Bruting/Griddling. This process requires attentiveness and expertise, in being able to shape the diamond precisely.
Bruting can be done through 3 different techniques such as bruting by lasers, rubbing the stone with other diamonds in the opposite directions, disks impregnated with diamond dust.
Bruting a diamond is an art and a science. In this process, the friction is produced in either way creating a rough grindle finish and progressively down the corners of the diamond round through abrasion.
Polishing of the diamond is the process of forming and shaping the facets of the diamond to achieve the optimum amount of reflection and refraction of the white light that brings sparkle and scintillation in the diamond.
In the blocking process, the main facets of the diamond including 8 pavilion, 8 crowns, 1 cutlet, and 1 table are formed; by placing a diamond into the tang and lowered on the scaife to polish the 4 main crown facets and 4 main pavilion facets.
Once polished, every single facet of each individual diamond is carefully revived by both a highly accurate laser scanner as well as by a trained gemmologist. Any diamond that doesn’t meet our strict quality control standards is sent back for re-polishing. The diamonds are then sent out to some of the most respected diamond grading laboratories worldwide such as GIA and IGI for certification before being studded in your precious diamond jewelry.
Our offerings are
as follows:
Loose Diamonds & Certified Gemstones
Round Brilliant Cuts and a wide range of Fancy Shapes such as Oval, Pear, Marquise, Princess, Cushion, Emerald, Radiant, Heart, and more
D to Z Color Grades along with a selection of Fancy Color Diamonds in various sizes and specifications
Available sizes range from 0.01ct to 30ct and beyond, catering to all preferences
